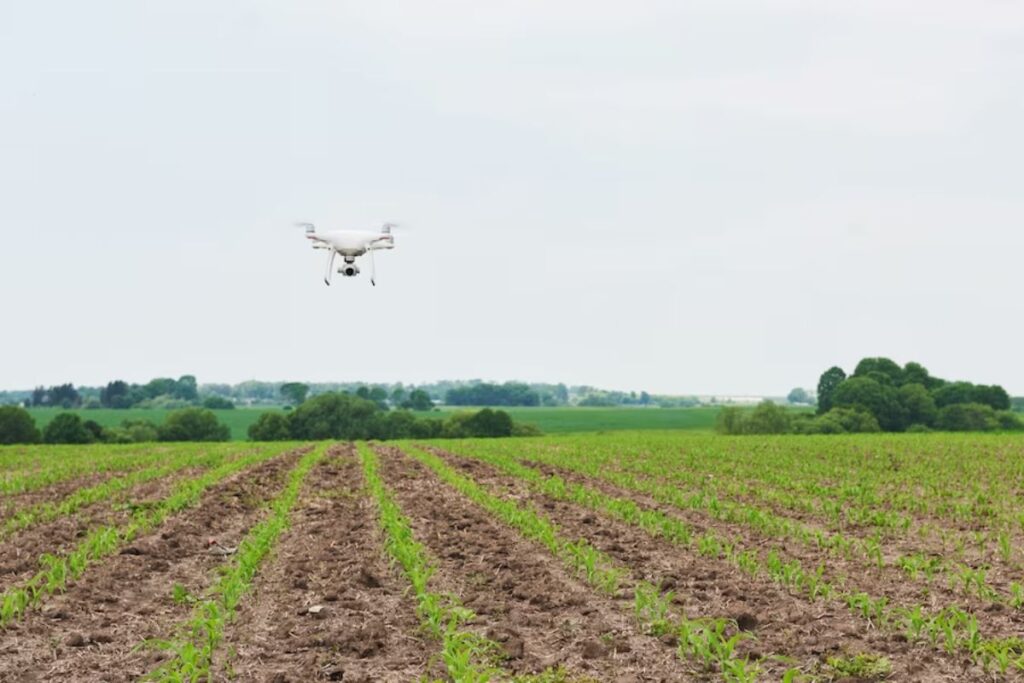
Drone use has been increasing rapidly in practically every industry in the country, but it is exploding in agriculture. According to some estimates, the agricultural drone economy will surpass $4.8 billion in 2024. Drones will be used for everything from surveillance to protection on large and small-scale farms in the coming years. The information obtained by drones on fields is typically used to influence agronomic judgments effectively and is an element of what is often known as ‘precision agriculture’.
Drones are becoming integral to large-scale precision agricultural systems in many places. The information from drones recording fields helps farmers plan their planting and operations to maximise harvests. According to some statistics, adopting precision farming technology can raise productivity by up to 5%, a significant increase in an economy with generally thin profit margins.
This blog will highlight the many aspects of drones in farming and their benefits.
The Use of Drones & The Agriculture Industry in India
Drones are unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) utilised for monitoring various sectors. They were previously primarily used by enterprises in industrial zones like mining and construction, the military, and hobbyist.
And drone technology is now becoming more widely available in various agricultural areas. Although the technology is still in its infancy in India, numerous businesses are working to make it freely accessible to Indian farmers and suitable for boosting agricultural productivity.
What role may drones play in Indian agriculture? First, drones boost general productivity, empower farmers to overcome other obstacles, and benefit from precision agriculture.
UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles) fill the gap left by human mistakes and inaccuracy in conventional farming practices, with the industry for agricultural drones exceeding a whopping $1.3 billion. Implementing drone technology aims to eliminate any uncertainty or guesswork and instead rely on accurate and dependable information.
Weather, soil quality, and temperature are all important aspects of farming. Agricultural drones enable farmers to respond to specific circumstances and make informed decisions.
The information gathered aids in crop health management, crop management, crop scouting, irrigation, field soil testing, and crop damage evaluations. The drone inspection improves crop production while saving time and money.
What Purpose Does the Agriculture Sector Need Drones For?
Drone technology will continue to advance in agriculture.
According to an ongoing study, the global agricultural drone industry will increase by 35.9% CAGR and surpass $5.7 billion by 2025.
Drone technology is going nowhere in agriculture. However, this developing innovation may assist farmers in saving time and boosting their efficiency. In addition, drone and Force Tractor use in agriculture will likely increase as the business evolves. Thus it is important to understand how to use this technology wisely.
-
Knowing About the Soil & Field Conditions
Drone field monitoring can also check the soil’s and field parameters’ health. Drones can give precise field modelling, including elevation data, allowing producers to detect anomalies in the area. Knowing the field’s elevation helps determine drainage patterns and wet/dry zones, enabling more effective watering tactics.
Several agricultural drone vendors and service providers utilising upgraded sensors also offer nitrogen level tracking in the soil. It allows for more precise fertiliser application, removing weak growing regions and boosting soil health for the years to come.
-
Crop Inspection
Crop surveillance monitors agricultural progress from the moment seeds are sown until maturity. It means implementing fertiliser at the appropriate time, inspecting for pests, and watching the impact of meteorological conditions. Crop surveillance provides the sole option for a farmer to secure a timely harvest, particularly with different vegetation types.
Any mistakes at this time can lead to crop damage. Crop surveillance aids in the comprehension and preparation for the upcoming farming season. Drones can assist in optimum crop surveillance by checking the farm with thermal imaging, and growers can take proactive steps to improve the state of the crops on the ground based on their reliable details.
-
Fertiliser Spraying
One of the most common applications of drones in farming is their capacity for moving fast to their targeted locations. Drones, with this ability, can sprinkle pesticides and fertilisers on crops to nurture and provide nourishment.
With such additives, crops can be productive and stay healthy. In addition, drone operators have complete power over the drone spraying micronutrients to prevent worms, parasites, and insects at bay and crop life extended.
-
Investigating the Flaws
Another amazing benefit of employing drones to fertilise crops is their capacity to look over, evaluate, and inspect these crops for flaws. In addition, their high-resolution imaging devices and sensors, also outfitted with lasers, assist in quickly completing numerous activities.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are being employed to map these faults in live time, and the data gathered and analysed can be used to make significant crop judgments.
-
Minimizes Environmental Impacts
Instead of spraying an entire field, which might have detrimental environmental effects, agriculture drones for spraying can provide pesticide and fertiliser spot solutions. Drones and New Holland Excel 4710 can contribute to reducing agricultural runoff and pesticide drift, which benefits surrounding crops and the soil.
Employing drones for spot operations instead of huge full-field sprayers or crop dusters can help mitigate air pollution while lowering farmer input costs.
Due to these benefits, drones are a strong competitor for improving agricultural processes at a competitive price. Besides the financial advantages, optimising fertiliser, pesticide, and water usage in critical aspects have other environmental and ecological benefits that would not be possible otherwise.
Conclusion
Drone technology has the potential to transform farming in the future. Numerous Indian businesses are also expressing interest in the market. They intend to invest in low-cost drones that assist farmers while creating employment possibilities for rural youngsters and improving farmer expertise.
Yet, the sector requires mature modifications considering the expanding population, farmer requirements, operational procedures, and dwindling farmlands. Furthermore, competent pilots are necessary to propel the still-untapped drone business ahead. Our farm owners and drone operators are the change-makers. Ultimately, observing where things evolve and how effective drone applications are in the long term will be fascinating.